
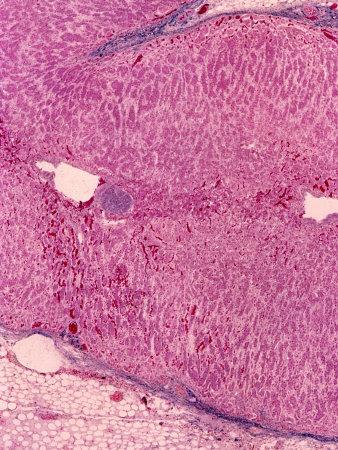

The two glands do, however, work together to produce and secrete hormones that help the body to respond to physical and psychological stressors. The adrenal cortex, conversely, produces hormones that regulate many processes in the body, such as metabolism, growth, immunity and sexual development. The adrenal medulla produces and secretes adrenaline and noradrenaline, which are primarily responsible for stimulation of the body’s fight-or-flight response.

The primary difference between the adrenal medulla and cortex is in the type of hormones that each of them produce and secrete. The adrenal cortex also plays an important role in responding to physical and psychological stressors.

Together, these hormones regulate a large number of bodily processes, such as metabolism, growth, immunity and sexual development. Finally, the adrenal cortex is involved in producing a number of androgens, including testosterone and androsterone, which are important in the development and maturation of male sexual characteristics. Mineralocorticoids such as aldosterone are responsible for regulating the body’s electrolytes and the reabsorption of sodium by the kidneys. Glucocorticoids, most notably cortisol, regulate the body’s metabolism and help to move water and nutrients around the body. These hormones can be divided into three classes: glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids and androgens. The adrenal cortex is the outer layer of the adrenal gland and is responsible for producing a variety of hormones that play a role in many bodily functions. Together, adrenaline and noradrenaline help the body to react to stressful situations. This chemical acts as a neurotransmitter, transmitting messages between neurons that can affect mood, sexual arousal, blood pressure, heart rate and others. In addition, the release of glucose into the blood stream helps to provide the energy needed to react to the situation.Īpart from adrenaline, the adrenal medulla also produces and secretes noradrenaline, a chemical similar to adrenaline but with different effects on the body. This is accomplished by increasing the heart rate, dilating the pupils, constricting blood vessels and increasing the rate of respiration. When exposed to a stressful or threatening situation, the body will produce adrenaline, which activates the body to react in a ‘fight-or-flight’ manner. Its primary purpose is to produce and secrete adrenaline, which is responsible for stimulating the body’s fight-or-flight response. The adrenal medulla is the inner portion of the adrenal gland.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
